Only Windows 11 from Pro version has the local group policy, Windows 11 Home has no group policy!►► to find and open the editor for group policy in Windows 11 is still possible Contents: 1.) ... group policy via Windows 11 search!
|
| (Image-1) Windows 11 have a group policy editor! |
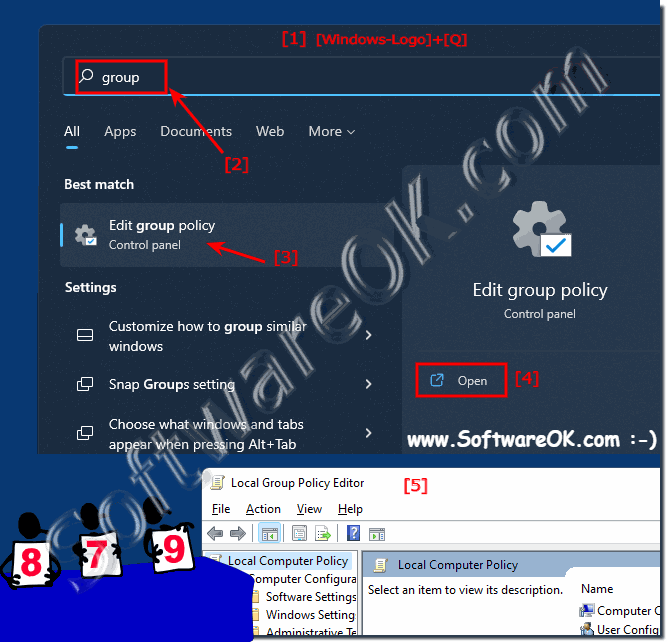 |
2.) More information about the group policies on Windows!
Group Policy is a powerful management tool in Windows 11 operating systems that allows administrators to centrally manage the configuration of Windows computers in a network environment. Here is some more information about Group Policy in Windows:
Purpose of Group Policy: Group Policy is used to control the security, configuration, and behavior of Windows operating systems in an enterprise environment. They can be used to manage user rights, software installation, desktop design, security policies, and many other aspects of the operating system.
Proper use of Group Policy requires a deep understanding of security considerations. Inadequate security configurations can create security vulnerabilities, so you should ensure that GPOs are securely configured.
Please note that using Group Policy requires advanced knowledge of Windows system administration. Incorrect configurations can lead to unexpected behavior and results, so it is important to carefully plan and test Group Policies before applying them in a production environment.
more tips:
► ... find and open the editor for group policy in Windows 11
Group Policies are an essential tool for managing Windows-based networks efficiently and securely. Understanding how to configure and use them effectively is crucial for system administrators responsible for network management and security.
► ... find and open the editor for group policy in Windows 11
► ... the group policy for Windows 11 and 10 Explorer!
► ... Force a group policy update on Windows with command line!
► ... The numerical file sorting under Windows 10/11 via group guidelines!
Group Policies are an essential tool for managing Windows-based networks efficiently and securely. Understanding how to configure and use them effectively is crucial for system administrators responsible for network management and security.
3.) For Windows 11 Home users who miss the Group Policy Editor!
In fact, Windows 11 Home Edition does not have a built-in way to manage Group Policies directly from the UI as it does not have the Group Policy Editor application (gpedit.msc) by default. The Group Policy Editor application is typically available in editions of Windows intended for enterprise use, such as: B. Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise and Education.For Windows 11 Home users who still want to use Group Policy Editor, there are a few alternative methods:
1. Registry Editor:
Many of the settings that can typically be adjusted through Group Policy are also available in the Windows Registry. Some of these settings can be made via the Registry Editor (regedit.exe). However, keep in mind that registry changes can be confidential and can cause problems if not done correctly. It is recommended to create backups and be careful before editing the registry.
2. Third-party tools:
There are also third-party tools that provide an interface for managing Group Policy settings and may have similar functionality to the Group Policy Editor. However, some of these tools are paid or require specific expertise.
3. PowerShell:
Some Group Policy settings can be applied via PowerShell commands. However, this requires knowledge of PowerShell and the specific commands to configure the desired settings.
It is important to note that changes to Group Policy settings can potentially affect the behavior of the system. You should therefore always exercise caution and ensure that you understand the impact of your changes.
4.) Advantages and disadvantages of group policy editors on Windows!
The Group Policy Editor on Windows provides a powerful way to manage and configure settings for users and computers on a network. Here are some pros and cons of using Group Policy Editor:Pros:
1. Centralized Management:
Group Policy Editor allows centralized management of settings for multiple users and computers on a network. This facilitates consistency and enforcement of policies across the organization.
2. Comprehensive Control:
Group Policy Editor allows administrators to set a variety of settings and policies, including security settings, desktop configurations, application restrictions, and more. This allows comprehensive control over the behavior of users and computers on the network.
3. Efficiency:
Group Policy allows administrators to make changes to settings for a large number of users or computers at the same time, which is more efficient than manually configuring each system individually.
4. Automation:
Group Policy allows automating routine tasks and enforcing policies without requiring manual intervention from users. This helps streamline operations and improve security compliance.
Cons:
1. Complexity:
Group Policy Editor can be complex for inexperienced users and requires a basic understanding of Windows system architecture and how Group Policy works.
2. Error susceptibility:
Incorrect configurations or misapplication of Group Policy settings can result in unexpected user or computer behavior and even lead to security risks.
3. User Resistance:
Users may show resistance to Group Policies, especially if they feel that their individual settings and customizations are being restricted.
4. User dependency:
The effectiveness of Group Policy depends on users being connected to the network and receiving the policies properly. If a user is offline or has network connectivity issues, Group Policy may not be applied correctly.
Overall, Group Policy Editor provides a powerful way to manage Windows systems on a network, but it requires expertise and careful planning to use effectively.
5.) Is the Group Policy Editor only available on Windows or are there other operating hours too?
Group Policy Editor is a feature designed specifically for Windows operating systems and is only available in versions of Windows intended for use in enterprise environments, such as. B. the Windows Professional, Enterprise and Education editions. Other operating systems such as macOS and Linux do not have a direct equivalent to Windows' Group Policy Editor.However, other operating systems also have mechanisms for centrally managing settings and configurations, although not in the form of a special “Group Policy Editor”. Here are some examples:
1. macOS:
macOS uses a feature called Profile Manager, which allows administrators to create profiles with settings for users and devices and manage them centrally. These profiles can contain a variety of settings, similar to Group Policy settings in Windows.
2. Linux:
Linux distributions often use configuration files and scripts to manage and configure settings. For the central management of Linux systems, there are various tools and protocols such as Ansible, Puppet and Chef, which allow administrators to manage and distribute configurations across multiple systems.
Although other operating systems do not have a directly comparable “Group Policy Editor”, they still offer mechanisms for centrally managing settings and configurations in corporate environments. These mechanisms vary depending on the operating system and may require different knowledge and tools to manage.
FAQ 86: Updated on: 27 April 2024 19:24
